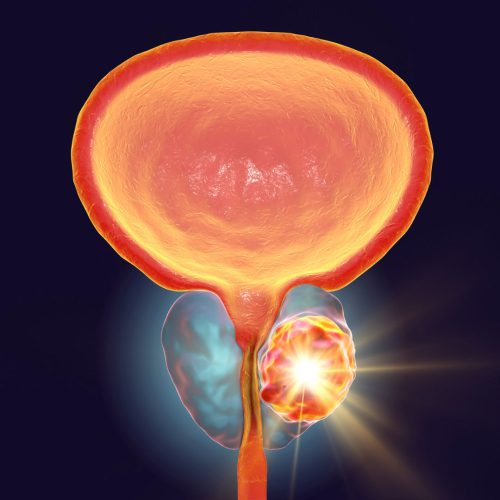
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is the most common prostate disease, about 25% of urologists work to treat BHP.
Benign (non-cancerous) enlargement of the prostate is caused by the growth of new prostate cells.
Symptoms
Weakening of the urine stream, difficulty starting urination, incomplete bladder emptying, frequent urination (day and/or night), urinary urge that cannot be suppressed. From epidemiological studies it is known that there are racial and genetic predispositions and that lifestyle and diet have some influence. Although histological signs of hyperplasia are already present in men in the fourth decade of life, BHP is of clinical significance only if LUTS (lower urinary tract symptoms) and clinical signs of subvesical obstruction occur.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made by measuring prostatic specific antigen (PSA) levels in patients with suspected BHP, and this analysis should be done on an annual basis in all men after the age of fifty-five, and especially in those with LUTS. Upper PSA normal limit is 4 ng/ml. The PSA value in this range does not rule out absolute certainty for cancer, especially for men under 60 years of age. PSA values above 10 require prostate biopsy to rule out prostate cancer. Values between 4 and 10 ng/ml are known as the “gray zone” and then the decision on a possible biopsy depends on the age of the patients, findings on rectal examination and history, primarily on the data on the existence of prostate cancer in relatives.
Therapy
Complications resulting from BHP can be urinary tract infections that are difficult to treat and often recur, urinary retention, blood appear in the urine, bladder and kidney damage (sand and stone formation), urosepsis. Therefore, it is very important to start therapy promptly to prevent the progression of the disease. BHP therapy and treatment is performed by a urologist after diagnosing the disease. In addition to taking recommended therapy, a moderate lifestyle and diet is recommended, the diet should be varied, rich in vitamins, moderately salty and spicy. It is important to avoid sitting and lying down for a long time, strenuously walking and cycling, it is important to urinate regularly, to avoid drinking large quantities of liquids at once, and to avoid drinking alcohol and cold drinks.